XML
You do not need to establish a connection to use the XML app.
Field | Description |
|---|---|
XML | Enter the source XML document. |
XPath Query | Enter the query in the XPath language. |
Converts a bundle to an XML formatted text.
Field | Description |
|---|---|
Data structure | Describes the structure of the resulting XML. If you have a sample of the XML you would like to parse, you can use it to generate the data structure:
|
A typical use case is to transform data from a Google spreadsheet into XML.
Place the Google Sheets > Select rows module in your to fetch the data. Setup the module to retrieve rows from your Google spreadsheet and set the Maximum number of returned rows to a small number, but larger than one for testing purposes (e.g. three). Run the Google Sheets module (right-click it and choose "Run this module only") and verify the output of the module.
Connect the Array Aggregator module after the Google Sheets module. In the module's setup choose the Google Sheets module in the Source node field. Leave the other fields as they are for the moment.
Connect the XML > Create XML module after the Array Aggregator module. The module's setup requires a data structure that describes the structure of the XML output. Click on Add to open the data structure setup. The easiest way to create this Data structure is to generate it automatically from an XML sample. Click on Generate and paste your XML sample to the Sample data field:
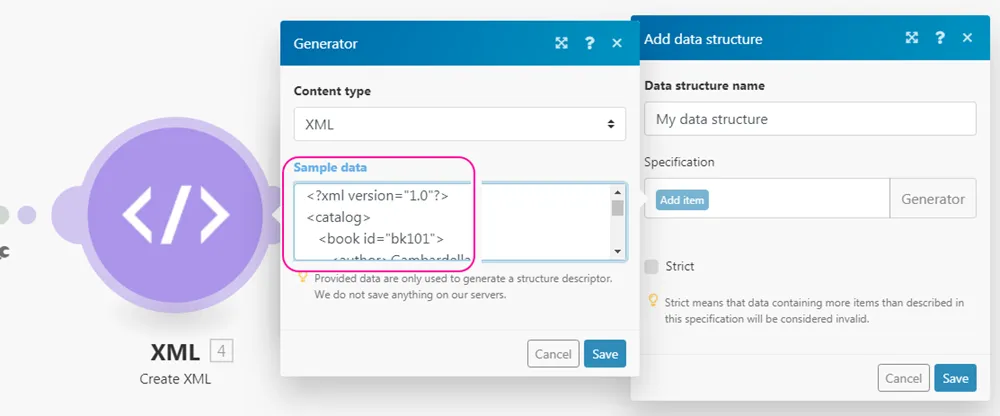
Click Save. The specification field in the data structure setup should now contain the generated structure.
Change the name of your Data structure to something more specific (e.g. "My XML data structure") and click Save. A field corresponding to the root XML element should appear as a mappable field in the XML module's setup.
Click Map next to the field and map the Array[] item output from the Array aggregator module.
Click OK to close the XML module's setup.
Open the setup of the Array Aggregator module. Change the target structure from Custom to an XML module's field corresponding to the parent XML element. Map items output from the Google Sheets module to appropriate fields.
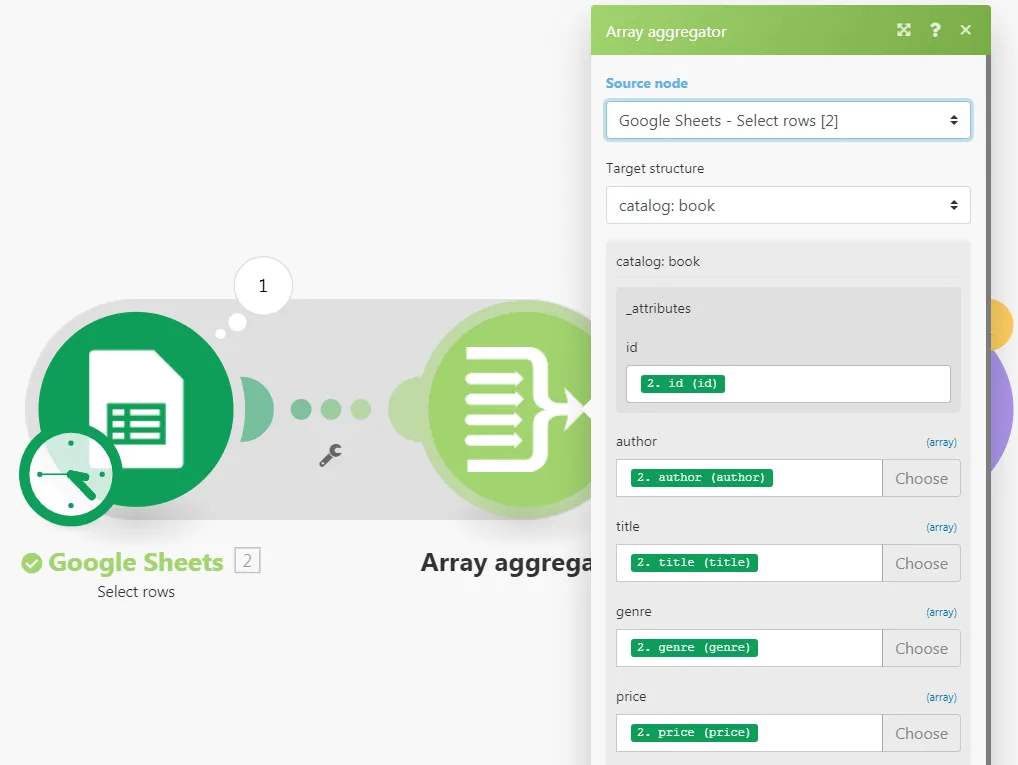
Click OK to close the Array Aggregator module's setup.
Run the scenario. The XML module should output the correct XML file. Open the setup of the Google Sheets module and increase the Maximum number of returned rows number to be larger than the number of rows in your spreadsheet to process all the data. The resulting XML can be then saved to Dropbox, sent as an attachment via email, uploaded via FTP to a server, etc.
If you want to add attributes to a complex node (a node, that will contain other nodes), you have to add a collection with the name _attributes for this node in your custom data structure, and this collection will be mapped to node attributes
If you want to add attributes to a text node (example: <node attr="1">abc</node>), you have to add a collection _attributes for attributes and a text property _value for the node value for this node in your custom data structure.
Parses an XML formatted text and outputs a single bundle containing all the information extracted from the XML.
Field | Description |
|---|---|
Data structure | Select or add a date structure. Describes the structure of the XML to make the output of the module available in the mapping panel for the modules that follow. If you have a sample of the XML you would like to parse, you can use it to generate the data structure:
You can skip steps 2-5 to supply an empty data structure. This way the output of the module will not be available in the mapping panel until the module has been executed at least once to process an XML input. |
XML | Enter the XML to parse. If you use a formula, make sure its result value type is (or can be automatically changed to) Text type. If the result value type is Buffer (binary data) then use toString() function to convert it to the Text type. |
A typical use case is to download an XML file from a URL and parse its content. Here is a step by step guide how to achieve this:
Add an HTTP > Get a file module.
Configure the module. Add the URL of the XML file.

Click OK.
Add the XML > Parse XML module, connect it after the HTTP > Get a file module and configure it.
Data structure field:
- Click Add.
- Click Generate
- In your web browser, open a new tab/window.
- Enter the URL you used in the third step in the address bar and fetch the XML file.
- Select all the XML text and copy it into the clipboard.
- Paste the copied XML text into the Sample data field.
- Click Save.
- Verify that the data structure has been successfully generated.
- Click Save to save the Data structure.
You can skip these steps to supply an empty data structure. This way the output of the module will not be available in the mapping panel until the module has been executed at least once to process an XML input.
XML field:
Map the Data item from the output of the HTTP > Get a file into this field. Use the toString() function to convert its value from Buffer (binary data) type to Text type.
You may copy and paste the formula's code into the field: {{toString(1.data)}}
By default, the XML > Parse XML module will put attributes in a special collection _attributes as a child of the node that has these attributes. If the node is a text node and it has attributes, then two special properties will be added: _attributes for attributes and _value for the text content of the node.
